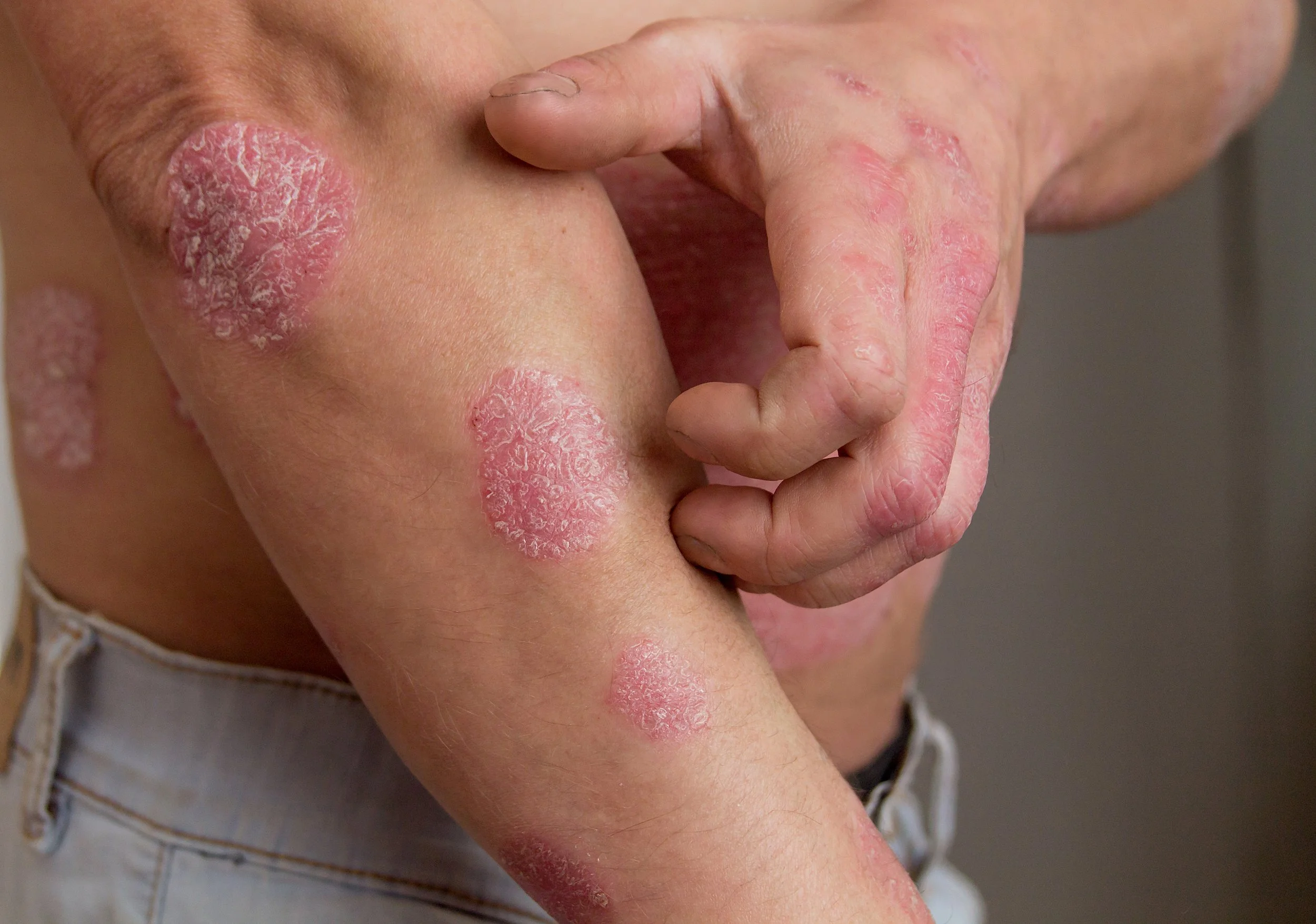
Psoriasis
A CHRONIC, IMMUNE-MEDIATED, INFLAMMATORY SKIN CONDITION CAUSED BY RAPID PRODUCTION OF SKIN CELLS, RESULTING IN THICK, SCALY PLAQUES.
The accelerated skin turnover leads to accumulation of scales and persistent inflammation.
It can affect individuals of all ages and tends to have periods of flare and remission.
Thickened, well-defined scaly plaques on the skin, Dry, cracked, itchy skin that may bleed, Scaly patches on the scalp resembling dandruff, Nail changes such as pitting, thickening, or discoloration, Joint pain or stiffness in some cases (psoriatic arthritis)
Symptoms
Treatments
❋ Topical Steroidal & Keratolytic FormulationsReduce inflammation and redness. Help remove thick scales and plaques. Used during flare-ups under medical supervision.
❋ Topical RetinoidsNormalize abnormal skin cell growth.
Improve plaque thickness and texture.
Often used in combination with other topical treatments.
❋ Barrier Repair CreamsRestore skin hydration and protect the skin barrier.
Reduce dryness, cracking, and itching.
Essential for daily maintenance therapy.
❋ Oral ImmunosuppressantsUsed in moderate to severe psoriasis.
Control immune overactivity responsible for flares.
Require regular monitoring under dermatologist guidance.
❋ Light Therapy (Under Supervision)Medically controlled phototherapy reduces inflammation. Slows excessive skin cell production. Effective for widespread or resistant psoriasis.
FAQs
-
Smoking
Alcohol consumption
Excessive sun exposure
Emotional stress
Certain medications
-
No, psoriasis is not contagious.
It does not spread through touch, shared personal items, or close contact.