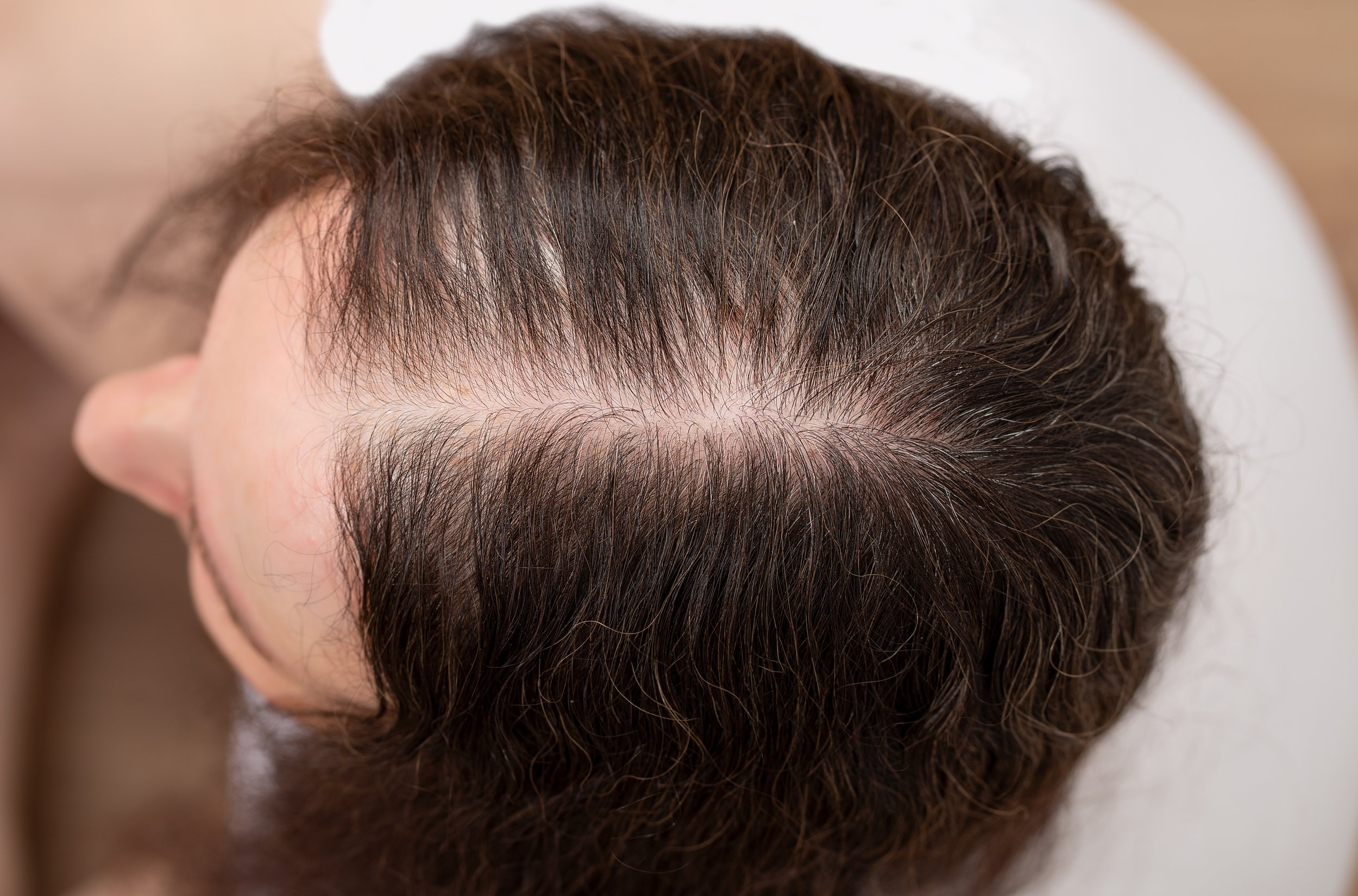
Hair Thinning
A COMMON CONDITION CHARACTERIZED BY GRADUAL REDUCTION IN HAIR DENSITY AND THICKNESS.
It results from a combination of genetic predisposition, hormonal influence, stress, and nutritional deficiencies.
This condition is medically termed male pattern baldness or female pattern baldness.
Gradual thinning of hair over months or years, Reduced hair volume and density, Increased scalp visibility, Miniaturization of hair strands, Progressive widening of parting (in women)
Symptoms
Treatments
❋ Topical & Oral Medical ManagementMedications to slow hair thinning and promote regrowth. Help stabilize hair loss and improve follicle function. Require consistent and long-term usage.
❋ PRP / GFC TherapyGrowth factor–based treatment to revive weakened hair follicles. Improves hair thickness and density. Used as standalone or supportive therapy.
❋ MesotherapyDelivers nutrients and hair growth stimulants directly into the scalp. Strengthens hair shafts and improves scalp circulation. Helps slow progression of thinning.
❋ Hair TransplantationPermanent solution for advanced hair thinning. Redistributes healthy follicles to thinning areas. Provides natural-looking, long-term results.
FAQs
-
Early-stage hair thinning can be controlled and partially reversed.
Advanced thinning may require procedural treatments like hair transplantation. -
Yes. Hair fall involves excessive shedding, while hair thinning is a gradual reduction in hair density due to follicle miniaturization.
-
Visible improvement usually starts after 3–6 months of consistent treatment.