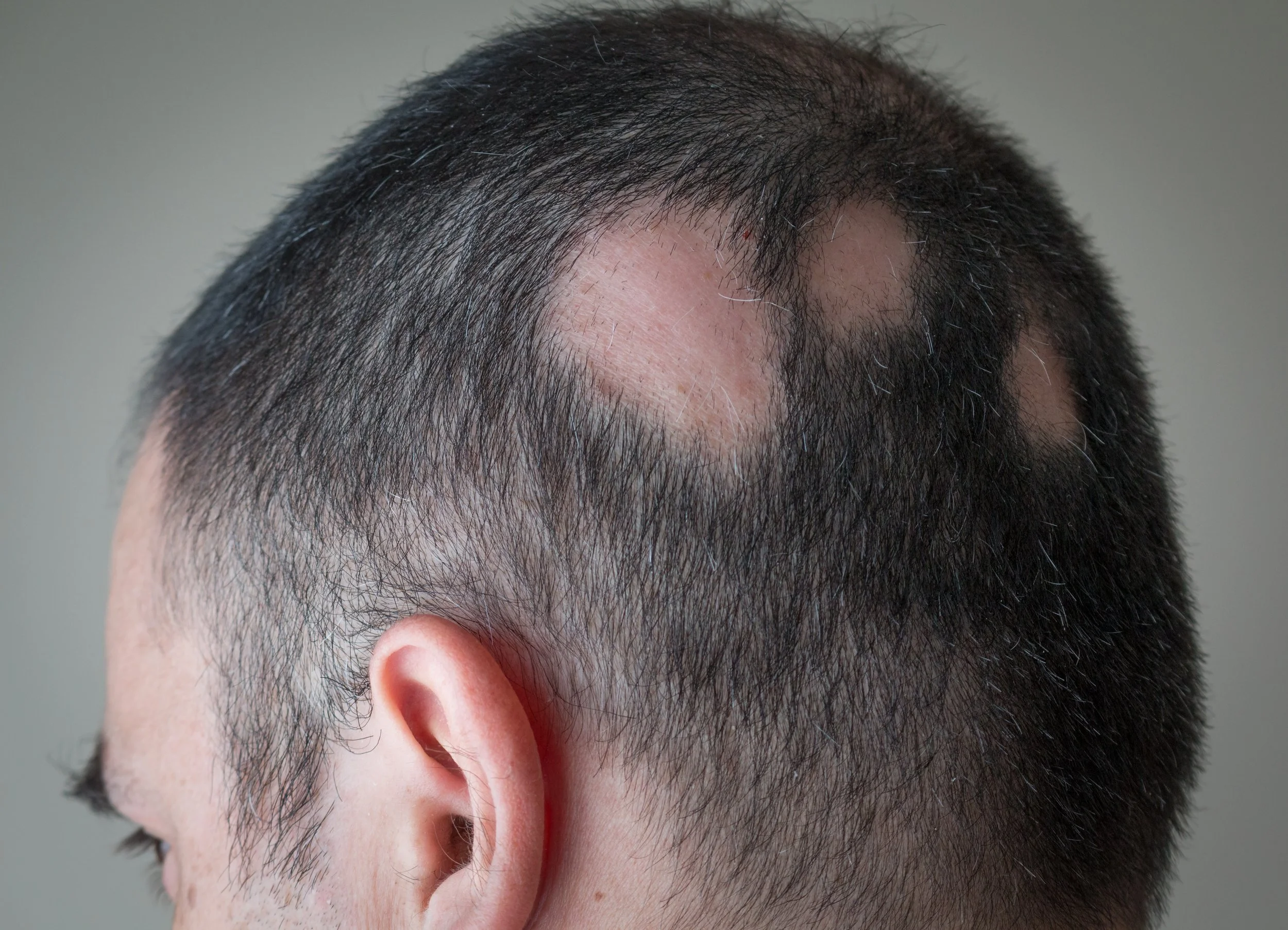
Alopecia Areta
AN AUTOIMMUNE DISEASE THAT CAUSES PATCHY HAIR LOSS ANYWHERE ON THE BODY.
It most commonly affects the scalp and beard but can involve eyebrows, eyelashes, and other hair-bearing areas.
Alopecia areata can occur in any age group, including children and adults.
Sudden patchy hair loss with well-defined bald patches,
Smooth, non-scarring skin over affected areas,
Hair thinning in the beard, eyebrows, or eyelashes,
Nail changes such as pitting in some patients
Symptoms
Treatments
❋ Topical & Oral TreatmentsMedications to suppress immune-mediated inflammation. Help stimulate hair regrowth and prevent progression. Customized based on severity and age.
❋ Intralesional Steroid InjectionsSteroids injected directly into bald patches. Reduce inflammation around hair follicles. Highly effective for localized alopecia areata.
❋ Light TherapyControlled phototherapy to modulate immune response. Stimulates hair regrowth in resistant cases. Administered under medical supervision.
❋ Lifestyle ModificationsStress management, nutritional optimization, and trigger control. Correction of underlying deficiencies if present. Personalized advice provided by the doctor.
FAQs
-
Alopecia areata is not a permanent condition as it does not cause scarring. With early intervention and treatment of the underlying cause, it is reversible in many cases.
-
Diagnosis is based on:
Hair pull test
Trichoscopy
Skin biopsy (if required)
Blood tests to identify underlying systemic or autoimmune conditions